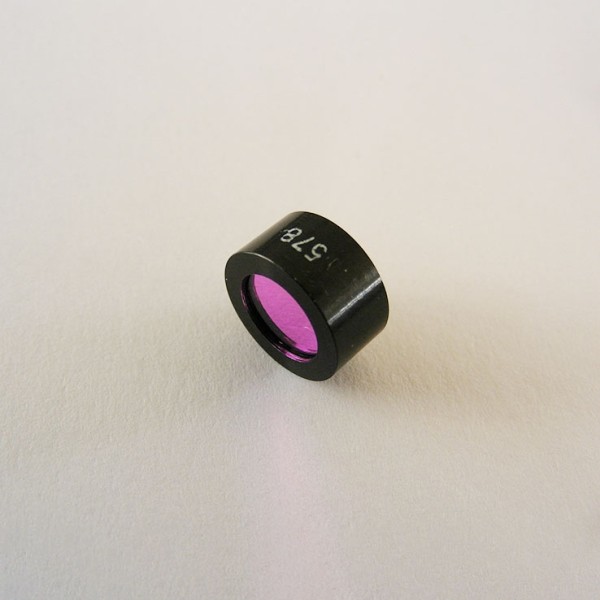
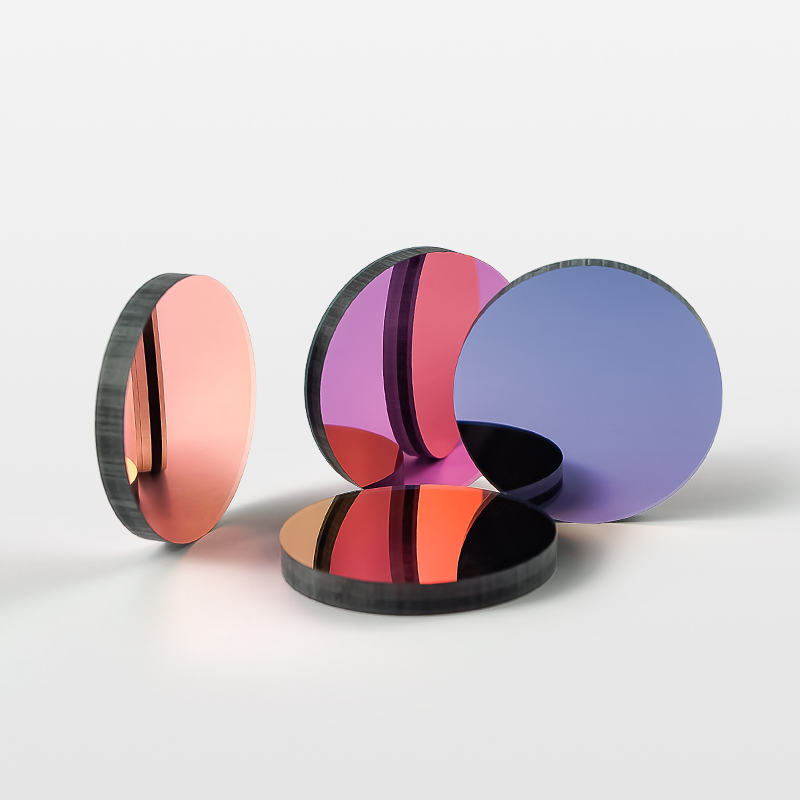
Biochemical analyzers are indispensable equipment in modern medical laboratories. They are used to detect various biochemical indicators in body fluids such as blood and urine, providing important basis for disease diagnosis. As one of the core components of biochemical analyzers, optical filters play a vital role in them.
Model:Optical Filters
Specifications: Customized
Material: Optical Glass

Product Introduction
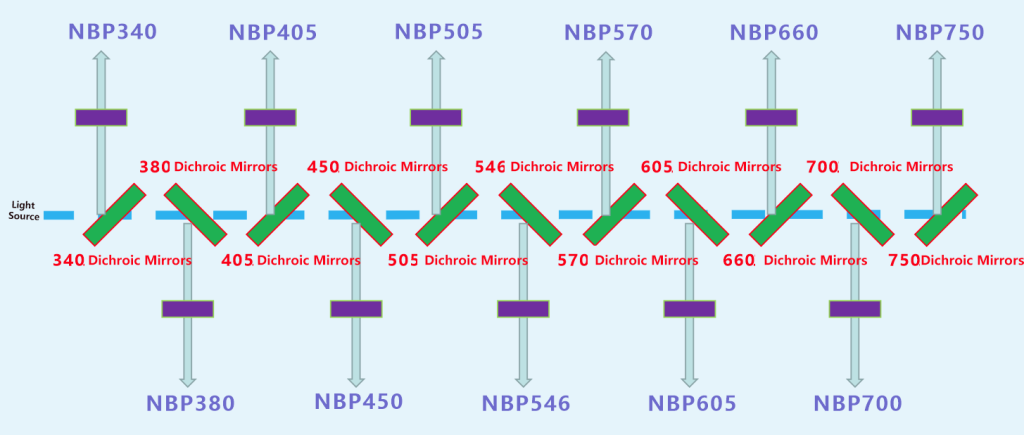
Application channels: 340nm 380nm 405nm 505nm 546nm 600nm 630nm 660nm 700nm 750nm 800nm
Optical indicators of narrowband filter:
Center wavelength: 340 and 380 channels, center wavelength deviation +/-1nm, center wavelength deviation of remaining channels +/-2nm
Peak transmittance: 340 channel greater than 55%, 380 channel greater than 60%, 405 channel greater than 70%, remaining channels greater than 75%
Cut-off depth: 200-1100nm Od5 or above
Half bandwidth: 8-10nm
Optical indicators of two-way beam splitter:
45° incidence, transmission area T>93%, reflection area R>95%, transmission and reflection covered channels, as long as the channel wavelength is ensured to be +/-3nm.
Collimating lens:
Applied at the front end of the optical system, including the reaction cup front lens and the reaction cup rear lens. Customized according to customer mold and internal optical path structure, designed according to customer needs.
Parameters include: outer diameter, center thickness, edge thickness, eccentricity, aperture, curvature radius, etc.
Transmittance wavelength characteristics (reference data)

Application
Biochemical analyzer: also often called biochemical analyzer, is an instrument that uses the principle of photoelectric colorimetry to measure a specific chemical component in body fluids. Due to its fast measurement speed, high accuracy, and small reagent consumption, it is now widely used in hospitals, epidemic prevention stations, and family planning service stations at all levels. The combined use can greatly improve the efficiency and benefits of routine biochemical tests.
Enzyme reader: It is a professional instrument for reading and analyzing the results of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (EIA) experiments. Through the enzyme-catalyzed color development coupled to the antigen or antibody, the concentration of the antibody or antigen to be tested in the sample can be judged by the depth of the color development, that is, the size of the absorbance value.
Optical path diagram