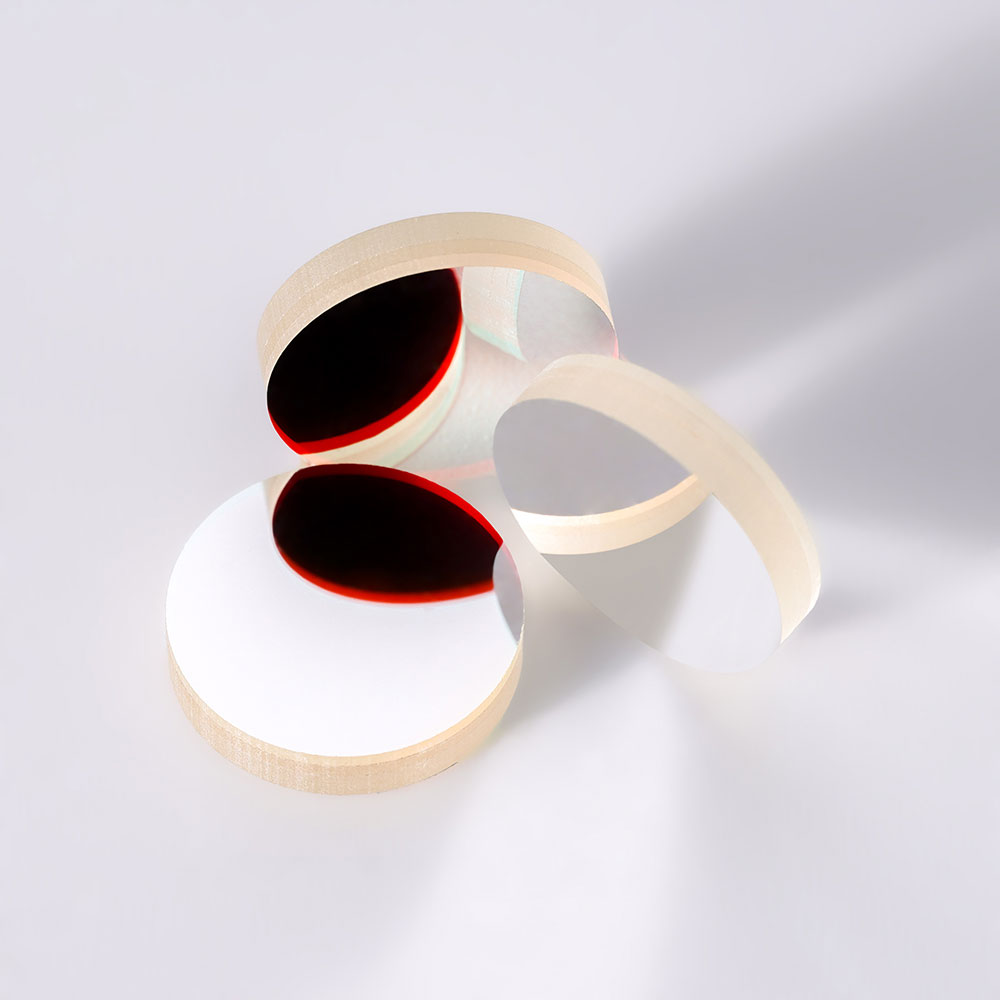
As the name implies, radial gradient neutral density filter is a filter whose optical density gradually changes along the radial direction. Its optical density gradually increases or decreases from the center to the edge, forming a continuously changing attenuation area. This filter can effectively control the intensity distribution of light and has a wide range of applications in photography, laser, optical measurement and other fields.
Model:Neutral Density Filters
Specifications: Customized
Material: Optical Glass
Product Introduction
Radial gradient neutral density filters (abbreviated as radial gradient density filters) can attenuate light intensity according to the trend of Gaussian function (or other functions). This type of filter can be used in natural light, laser and other fields, and can be used in the spectral range of 250nm-2500nm.
Working principle of radial gradient neutral density filter
The attenuation effect of radial gradient neutral density filter is achieved by depositing metal or dielectric films of different thicknesses on a glass substrate. The thickness of the film layer determines the degree of light absorption in that area, thus forming a gradient of light density.
Features of radial gradient neutral density filters
Continuous gradient: The optical density changes continuously in the radial direction without obvious steps.
Flexible customization: The gradient range, optical density range and other parameters can be customized according to different application requirements.
High transmittance: It has high transmittance in the non-attenuation area.
Good durability: It has good mechanical properties and environmental adaptability.
Classification of radial gradient neutral density filters
According to the gradient direction:
Center dark: the light density gradually increases from the center to the edge.
Center bright: the light density gradually decreases from the center to the edge.
According to the gradient curve:
Linear gradient: the light density changes linearly with the radius.
Non-linear gradient: the light density changes nonlinearly with the radius, such as Gaussian distribution.
Technical Parameters
| Substrate | BK7、Fused Silica |
| Outer diameter | 25mm、50mm |
| Outside diameter tolerance | +0/-0.15mm |
| Thickness tolerance | ±0.1mm |
| Parallelism | 3 ’ |
| Standard linearity | ±5% |
| Standard deviation of the darkest point of optical density | ±5% |
| Surface quality | 80-50 |
| Calibration wavelength | 550nm |
| Design wavelength | 380nm-2000nm (BK7)250nm-2500nm(Fused Silica) |
Standard products
| Outer diameter | Dark Zone | OD | Substrate |
| 25 | center | 1 | BK7 |
| 25 | center | 2 | BK7 |
| 25 | center | 3 | BK7 |
| 25 | center | 4 | BK7 |
| 50 | center | 1 | BK7 |
| 50 | center | 2 | BK7 |
| 50 | center | 3 | BK7 |
| 50 | center | 4 | BK7 |
| 25 | edge | 1 | BK7 |
| 25 | edge | 2 | BK7 |
| 25 | edge | 3 | BK7 |
| 25 | edge | 4 | BK7 |
| 50 | edge | 1 | BK7 |
| 50 | edge | 2 | BK7 |
| 50 | edge | 3 | BK7 |
| 50 | edge | 4 | BK7 |
Applications of Radial Gradient Neutral Density Filters
Photography: Used to control the exposure of different areas in the picture and improve the dynamic range of the picture.
Laser: Used to homogenize the energy distribution of the laser beam and improve the quality of the laser beam.
Optical measurement: Used to calibrate the nonlinear response of the optical system.
Solar cells: Used to improve the efficiency of solar cells.