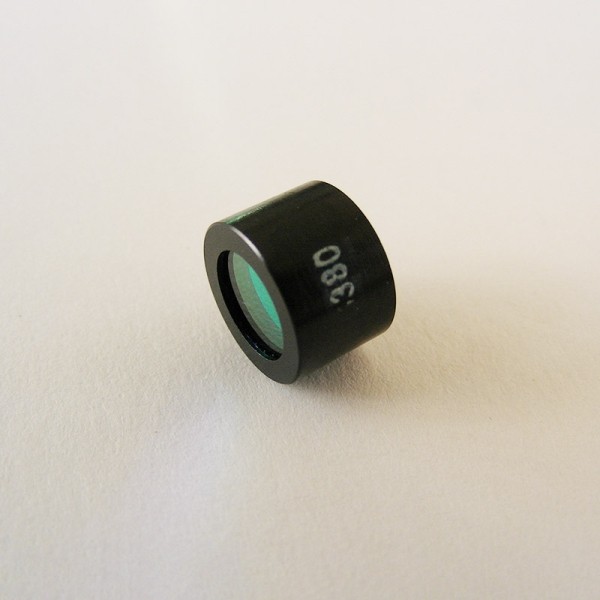
An infrared variable neutral density (IR VND) filter is a type of optical filter designed to control the intensity of infrared (IR) light in a tunable, continuous manner. This type of filter is primarily used in infrared imaging, sensing, and laser applications to attenuate IR light without affecting its wavelength or spectral properties. It functions similarly to a standard neutral density filter but is engineered specifically for the infrared spectrum, typically for wavelengths from 700 nm (near-infrared) up to several micrometers, depending on the application.
Model: IR VND filter
Specifications: Customized
Material: Optical glass
How an Infrared Variable Neutral Density Filter Works
The IR VND filter typically consists of two polarizing films or elements with adjustable relative rotation. The filter’s density—and thus the level of light attenuation—can be varied by rotating these polarizing elements relative to each other. In the “open” position, the filter allows maximum light transmission, while rotating the elements reduces transmission by increasing the density, allowing fine-tuned control over light intensity.
Key to its design, the materials used are selected to remain effective in the IR region, unlike standard VND filters, which are usually optimized for visible light. This ensures minimal impact on IR wavelengths and optimal attenuation across the specified range.




Key Features of an Infrared Variable Neutral Density Filter
Wavelength Range: Designed for the infrared spectrum, covering specific ranges like near-infrared (700 nm to 1,200 nm), mid-infrared, or even extended ranges up to around 5 micrometers, depending on the material and construction.
Continuous Attenuation: Allows for smooth, variable control over the intensity of IR light, typically achieving attenuation values from nearly 100% transmission down to below 0.1% transmission.
Minimal Spectral Shift: Attenuates IR light uniformly across the specified range, maintaining the integrity of the wavelength characteristics without introducing a spectral shift.
High Transmission Quality: Ensures that the transmitted IR light maintains high optical quality, often essential for applications in imaging, spectroscopy, and laser systems.
Advantages of Infrared Variable Neutral Density Filters
Adjustable Attenuation: Provides flexible control over IR light intensity, allowing continuous tuning to suit various applications and lighting conditions.
Uniform Attenuation Across the IR Spectrum: Designed specifically to maintain a neutral effect on IR light, allowing accurate spectral imaging and measurement without distortion.
Versatility: Works with a variety of IR wavelengths, making it suitable for multi-wavelength applications where precise control over IR light intensity is critical.
Enhanced Image Quality and Safety: By reducing glare and managing IR light levels, IR VND filters improve the quality of IR images and reduce risks associated with high-intensity IR exposure, particularly in laser applications.
Applications of Infrared Variable Neutral Density Filters
InInfrared Imaging and Cameras:
- In IR cameras, an IR VND filter enables controlled exposure to optimize image quality across different lighting conditions, especially in surveillance, thermal imaging, and scientific imaging.
Spectroscopy:
- IR VND filters are used in IR spectroscopy systems to control the intensity of IR sources, which helps in obtaining accurate spectral measurements without saturating the detectors.
Laser Systems:
- IR lasers often require fine-tuned power control. An IR VND filter can attenuate laser intensity, making it safer and more effective for use in alignment, measurement, and material processing.
Material Testing and Analysis:
- In fields such as material science and engineering, IR VND filters allow controlled IR illumination for testing the thermal properties, reflectance, or absorption characteristics of materials.
Scientific Research and Environmental Monitoring:
- For applications that require precise IR light control, such as environmental sensing or chemical analysis, IR VND filters enable accurate, repeatable measurements in changing light conditions.
Medical and Biological Imaging:
- IR imaging and spectroscopy in medical diagnostics benefit from the controlled IR intensity that VND filters provide, especially in applications like tissue imaging, where light penetration must be managed carefully.
Photography and Optical Instruments:
- Polarizing films are used in scientific instruments to control light reflections and improve visibility in complex optical systems. In lasers, they help manage light paths and are essential for many optical experiments requiring specific polarization states.
Product parameters (reference data)
| Product Name | Shaped reflector infrared variable neutral density filter |  |
| Working band | 3-5μm | |
| Density tolerance | ±5% | |
| Clear Aperture | >90% | |
| Inner diameter tolerance | +0.15/-0mm | |
| Outside diameter tolerance | +0/-0.15mm | |
| Parallelism | 3’ | |
| Surface quality | 60-40 | |
| Optical density gradient range | OD0-OD4 |