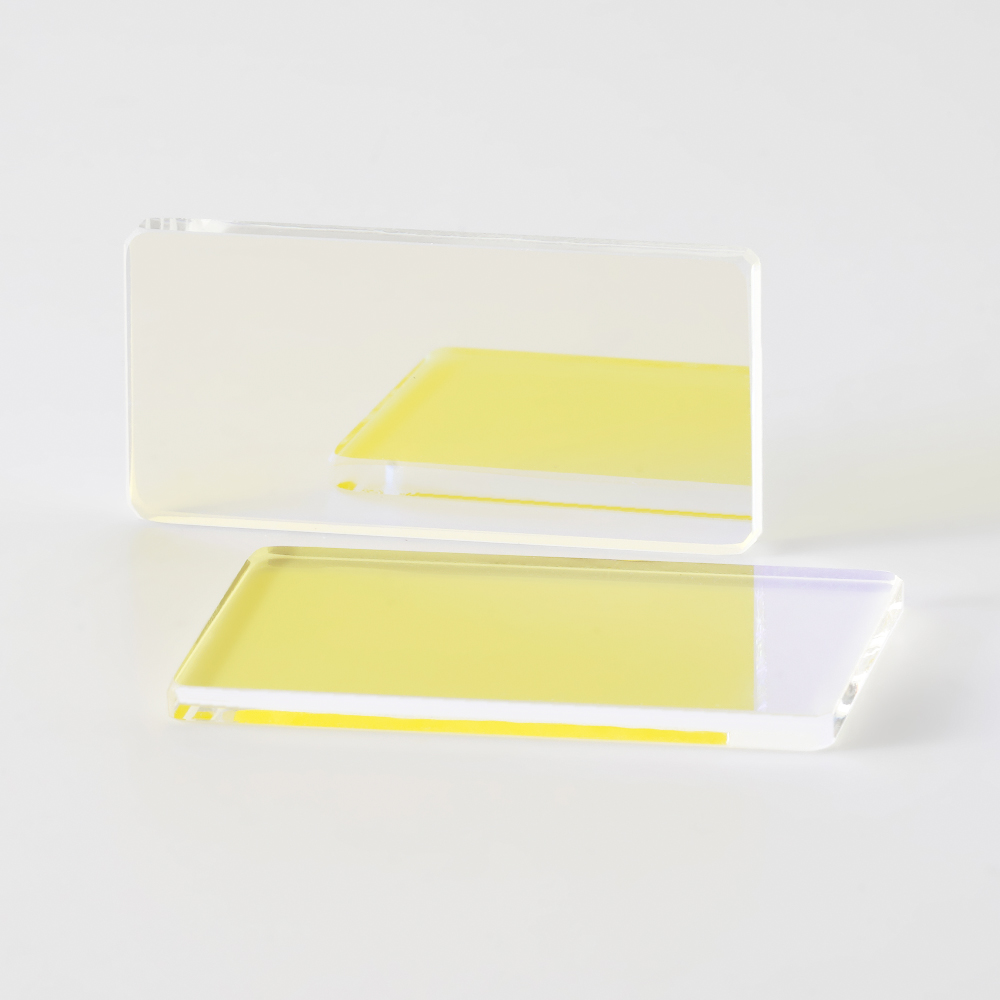
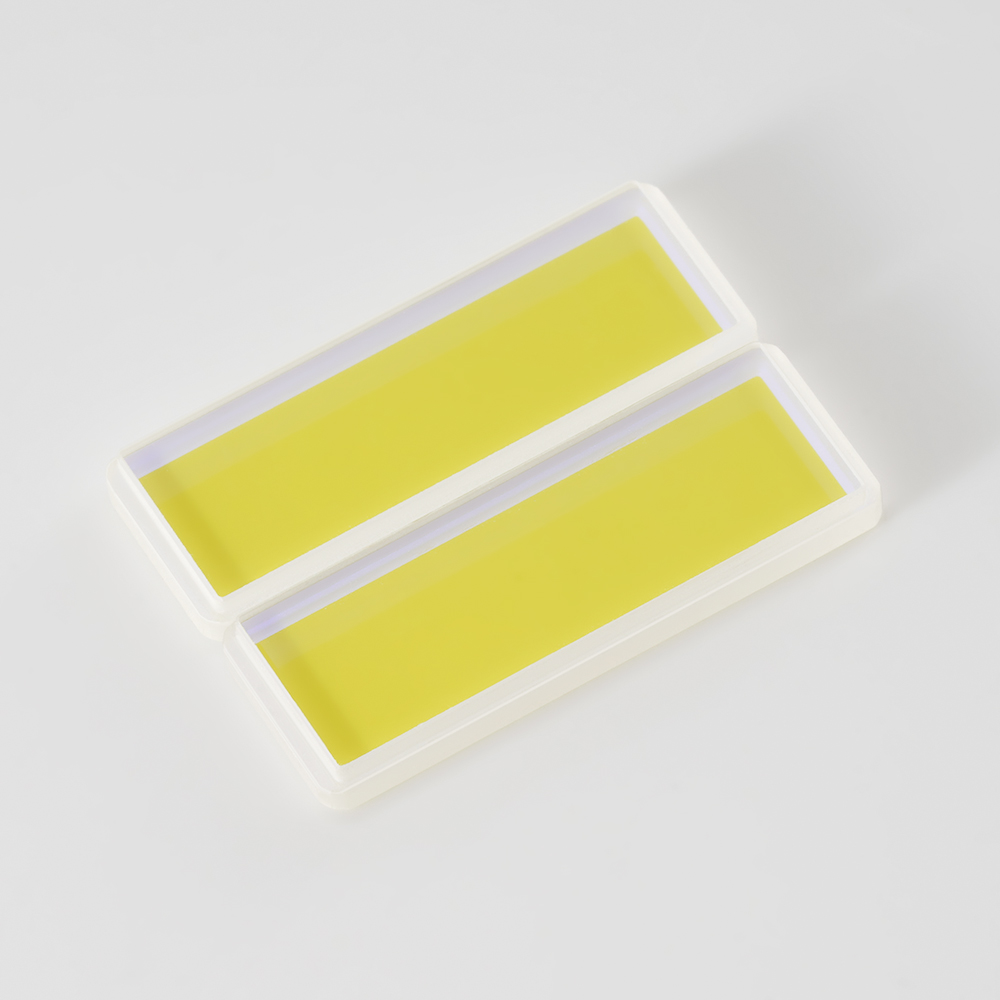
This filter is a multi-spectral array filter that is precisely made using a coating composite process. The high-performance filter film for each spectral band is plated with precise nanometer, high-transmittance and deep-cutoff coating technology. It has excellent filtering characteristics, multiple filter channels are integrated into a single substrate, and the spatial position alignment accuracy is extremely high.
Model: Multispectral filters
Specifications: Customized
Material: Optical glass
Product attributes
Material: optical grade glass
Transmittance: T≥90%
Size: customizable
Wavelength range: 400nm~1100nm
Main Features



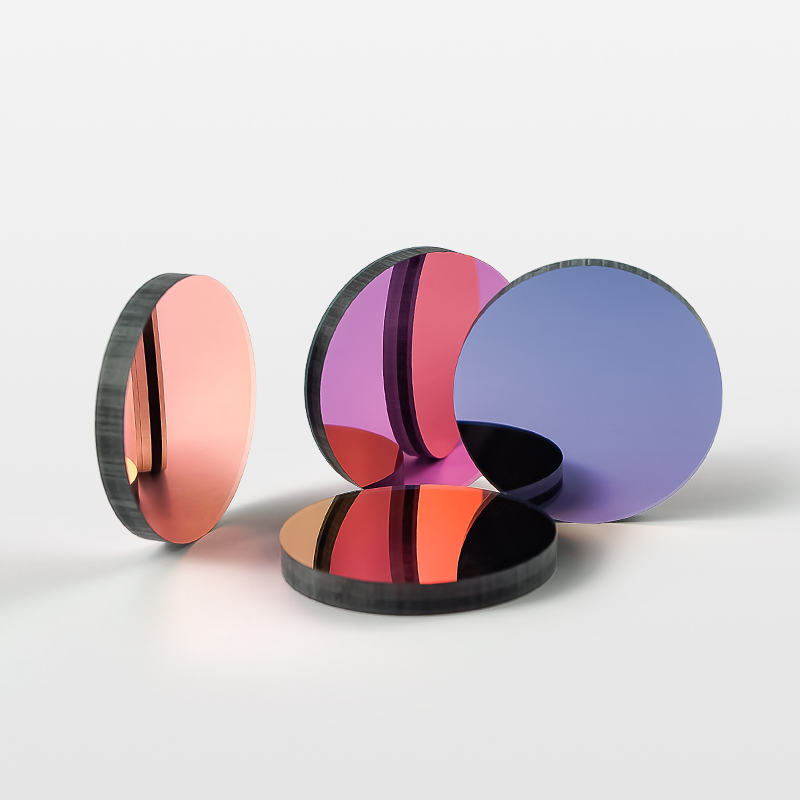
Broadband selectivity: Multispectral filters are able to allow light in specific bands (visible light, infrared, ultraviolet, etc.) to pass through while effectively blocking light in other bands. This allows them to selectively transmit multiple spectral components according to different needs.
Band separation: These filters can be designed as bandpass, shortpass, or longpass filters, depending on the wavelengths that need to be isolated. For example, bandpass filters can be used for the selection of specific spectral bands, and longpass or shortpass filters are used to select larger or smaller wavelengths of light.
Multi-channel filtering: Some multispectral filters combine multiple filters in a single optical device to process multiple wavelength channels simultaneously, supporting multi-channel imaging or detection systems.
Precise spectral separation: Due to their high selectivity and accurate band separation, multispectral filters can effectively reduce crosstalk between different wavelengths and improve the accuracy and resolution of imaging or analysis.
Multi-spectral filter transmittance wavelength characteristics (reference data)

Applications
Multispectral imaging: used to capture information in different bands, widely used in medical imaging, agriculture, remote sensing and other fields. Multispectral filters can accurately distinguish different spectral data to help analyze the composition, health status or environmental changes of objects.
Fluorescence microscopy: used in multiple fluorescent labeling experiments to ensure accurate acquisition of signals from different dyes or markers to avoid wavelength crossover and crosstalk.
Spectral analysis: used to extract light in a specific band from complex spectral signals, often used in chemical analysis, environmental monitoring and other fields.
Remote sensing and satellite imaging: through precise band selection, help analyze different features of the surface (such as vegetation, water bodies, urbanization, etc.).